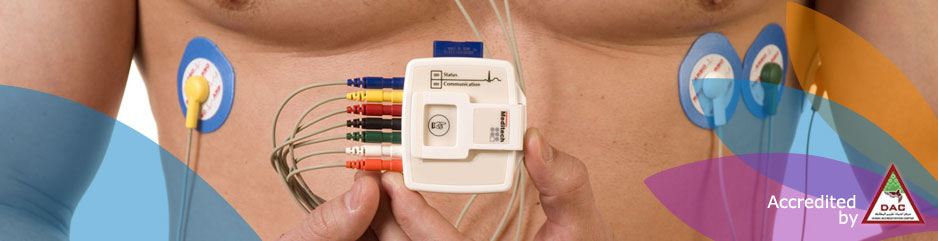
Holter Monitor
(24-hour ECG or long-term continuous electrocardiographic recording)
Purpose
To record heartbeats over an extended period, during normal activities - which may identify problems undetected by an electrocardiogram.
How it works
A portable ECG monitor is connected to ECG leads attached to your chest to measure and record the pathway of electrical impulses through the heart muscle.
Preparation
- ECG leads are attached and taped in place to prevent displacement. Chest hair may be shaved.
- The monitor is usually worn in a shoulder harness or can be carried in a pocket or attached to your belt.
Test procedure
- A continuous ECG is made as you go about your daily activities.
- You may carry out normal, everyday activities, but be alert to irregular heartbeats, chest pains, and other symptoms.
- Keep a careful diary recording your various activities (exercise, eating, etc.), and record the time and circumstances of any symptoms. Some monitors allow this to be done electronically, highlighting specific portions of the ECG recording during the symptoms.
- Don't let the leads get wet. If a lead comes loose, don't try to reattach it yourself. Go to the lab or doctor's office to have it reattached.
After the test
You return to the doctor's office or lab to have the monitor and leads removed.
Factors affecting results
- Mechanical failure such as battery malfunction, a faulty monitor, scratching, or moving a lead.
- Use of certain drugs--legal or illicit--that can alter heart rhythms.
- Stress, hyperventilation (over breathing), exercise, and straining (these activities should be recorded in your diary).
Interpretation
The ECG recording is scanned by a computer for abnormalities; abnormal recordings, along with your diary of activities, are reviewed by a doctor.
Advantages
- It allows ECG monitoring over an extended period and is used to detect heart rhythm disturbances.
- It can be used by people who cannot undergo exercise stress tests to detect intermittent serious heart problems such as intermittent arrhythmias and silent ischemia (periods of insufficient oxygen supplied to the heart muscle) occurring during normal activities.